Reviewed-on: artixweb/artixweb_packages#16
ArtixWeb Packages
ArtixWeb Packages contains the official Artix repo packages web application crates and service used to power artix packages website.
Installation
The easiest way of installing the solution is by using the provided Installation Dockerfile to build a docker image that you can deploy into a Docker Swarm, Docker Composer or any other container orchestrator of your choice.
There are composer and swarm configuration templates in the example_files directory that you can use to base your configuration on, those examples are fully documented on their own
Below you can find a detailed step by step guide on how to do so
Cloning the repository
First we need to clone this repository locally, for that we will need the git package from artix's world repository if we do not have it yet
During this document
doaswill be used instead ofsudo, obviously, you can use whatever fits you
cd ~
mkdir -p projects/artix
git clone https://gitea.artixlinux.org/artix/artixweb_packages.git projects/artix/artixweb_packages
The command above will make a local clone of this repository in $HOME/projects/artix/artixweb_packages, if you prefer your copy to reside in some other location in your har drive just clone it wherever you like instead
Building the Docker Image
For building the Docker image we need the docker package from the galaxy repository to be installed, proceed to install it if you don't have it yet
cd ~/projects/artix/artixweb_packages
docker build -f Dockerfile.install -t artixweb-packages:latest .
The command above will generate a new Artix based container with the latest version of the application ready to be deployed on any Docker server
Deploying the Service
Now that we have a container we will be able to deploy it to any Docker capable service. The service has a few requirements that must be spinned up along side, how do you choose to architecture the whole solution is up to you, follow the example docker compose file in the example_files directory to learn more about the service dependencies.
To start the provided composer example, just cd into example_files and run:
docker compose up -d
Refer to the
exmple_files/docker-compose.ymlfile for further explanations, it is fully documented
Environment Variables and Options
The service is configured just passing options to its command line, with environment variables or with a mix of both
Note
: some configuration options are only available as environment variables
Artix Linux Packages Information Website
USAGE:
artixweb_packages [OPTIONS] --key <SESSION_KEY> --smtp_user <SMTP_USER> --smtp_pwd <SMTP_PWD> --smtp_relay <SMTP_RELAY>
OPTIONS:
-b, --bind <BIND_ADDRESS> [env: BIND_ADDRESS=] [default: 127.0.0.1]
-d, --domain <DOMAIN> [default: localhost]
-h, --help Print help information
-k, --key <SESSION_KEY> [env: SESSION_KEY=]
-p, --port <PORT> [default: 1936]
--smtp_pwd <SMTP_PWD> [env: SMTP_PWD=]
--smtp_relay <SMTP_RELAY> [env: SMTP_RELAY=]
--smtp_user <SMTP_USER> [env: SMTP_USER=]
-u, --databaseurl <DATABASE_URL> [env: DATABASE_URL=] [default: localhost]
-v, --verbose
-V, --version Print version information
By default, the service binds to the loopback interface, this means that it will not allow connections from outside the Docker container, so we have to bind it to 0.0.0.0
This binds by default on
loopbackin case users prefer to run the service in real hardware behind anginxproxy or similar
The -k and --key options or SEESION_KEY environment variable is used to provide of a 256 bits key (as an hex string) that will be used by the application to cipher and sign session cookies
Recommended to use Docker secrets for this or any other vaulting solution
The -u and --databaseurl or DATABASE_URL environment variable is used to provide a valid PostgreSQL database URL for the service to connect to, this database is used to store package metadata and package flags information as well as the local service users. An example of DATABASE_URL could be postgres://user:password@db.url.com/artix_packages
For email sending, smtp options must be provided, the -smtp_relay is the address of a valid SMTP server that is listening in secure TLS port. If the SMTP connection fails for any reason, the service tries to use an unencrypted localhost connection to a SMTP server running in port 25, this will most likely fail in a Docker container solution (unless you install an SMTP server in the container that is unlikely to happen).
The rest of the options in there are self explanatory and does not require of further documentation
Environment Variables Only
Users should also provide an API_TOKEN that will be used to authenticate API requests that have administrative or special purpose. The token can be any string of any length, we recommend a sha256, for example, a sha256sum of 4MB of random data from /dev/urandom like
dd if=/dev/urandom bs=8b count=1024 iflag=fullblock 2>/dev/null | sha256sum | awk '{print $1}'
This token must be provided to any administrative like endpoint (usually using curl or similar)
Optional Environment Variables Only
There are some optional environment only variables that can be adjusted as well to configure the service behavior, they get listed below:
APP_NAME: used to set up the web site title, defaults toArtixWeb PackagesGITEA_URL: used to set up the URL to the Artix's gitea service, defaults tohttps://gitea.artixlinux.orgGITEA_API_URL: used to set up the URL to the Artix's gitea API service, defaults tohttps://gitea.artixlinux.org/apiGITEA_TOKEN: used to set up the gitea token, defaults to empty stringDATABASES_PATH: used to set up the path of the pacman databases the service uses, defaults to/var/lib/pacman
Creating DB schema
For easy DB schema creation an adminer container is included in the composer file.
The user can also just copy the
schema.sqlfile in theexample_filesdirectory to the running postgres container and usepsqlcommand from the postgres-libs package instead
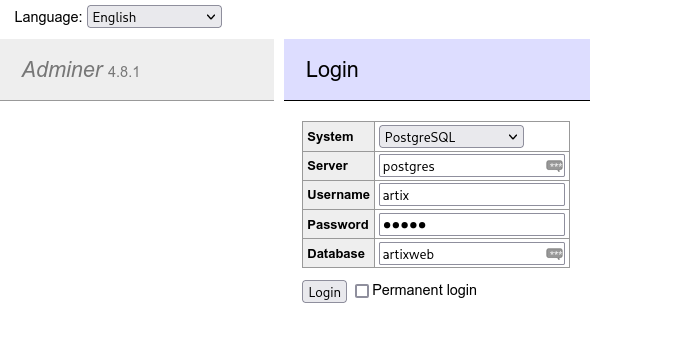
Point your browser to http://localhost:8080 and login into the database, if you did not made any changes to the docker-composer.yml file it will looks like the screenshot below
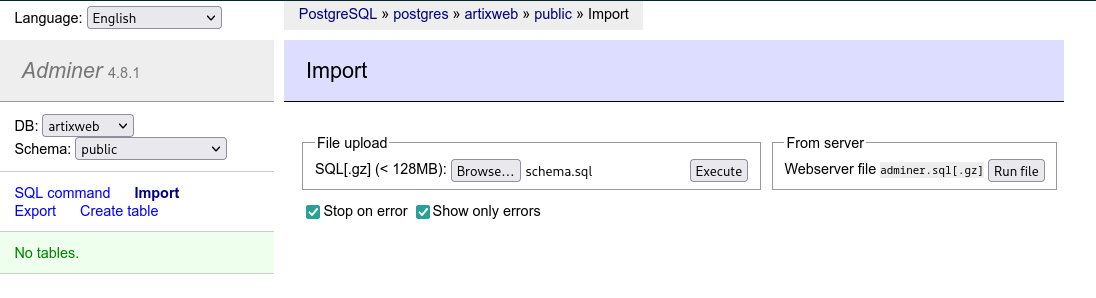
After login in, click on the Import link on the left side menu and select the example_files/schema.sql file from the project
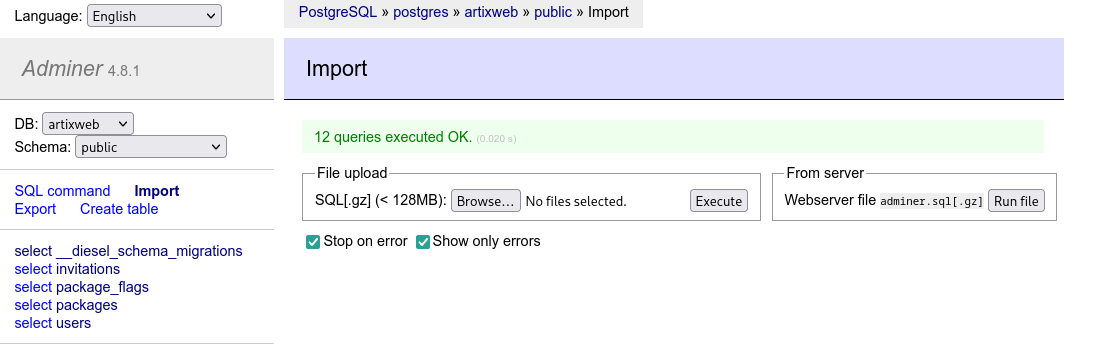
Just click the Execute button to import the database schema
As a last step and to make sure everything is fine, restart the stack using the following command inside the example_files directory
docker compose restart
You should now be able to access the ArtixWeb packages web interface in http://localhost:8000
How it works?
ArtixWeb Packages works using a combination of libalpm and gitea API queries, the first time that a package detail is check by anyone, the metadata extracted from gitea API gets pushed into a local postgres database that is used both to cache/store relational packages metadata/information and users storage.
How to flag a package?
Only trusted users that have an account can flag packages, any non authenticated user will be unable to access the flagging packages UI unless they are properly authenticated into the service. Packages can be flag just by entering its details and clicking in the Flag package out-of-date link in the right side Actions Panel.
Note
: the only user data stored in the service database is the user email, that is used to authenticate within the service, the email is necessary because it is used to send admin created invitations via email, users use the link on the invitation email to register into the service, the email is not used for any other purpose and users or activity is not being track in any way
How to un-flag a package?
Packages will be automatically un-flagged as soon as a new version is pushed into the Artix stable package repositories and the service syncs it.
Manually un-flag
Users being in possession of the API_TOKEN that the service is using can manually un-flag any package using a curl request
curl -X DELETE \
-H "X-Admin-Token: <token>" \
https://packages.artixlinux.org/akonadi/21.12.3-2
How to create an invitation?
Being in possession of the API_TOKEN that the service is currently using, one can use curl to create a new invitation and send an invitation email
curl -X POST \
-H "X-Admin-Token: <token>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"email":"user@email.com"}' \
https://packages.artixlinux.org/api/invitation
The service will use the configured SMTP access in order to send the email to the user, if the email can not be send, the invitation ID will be printed into the service logs output.